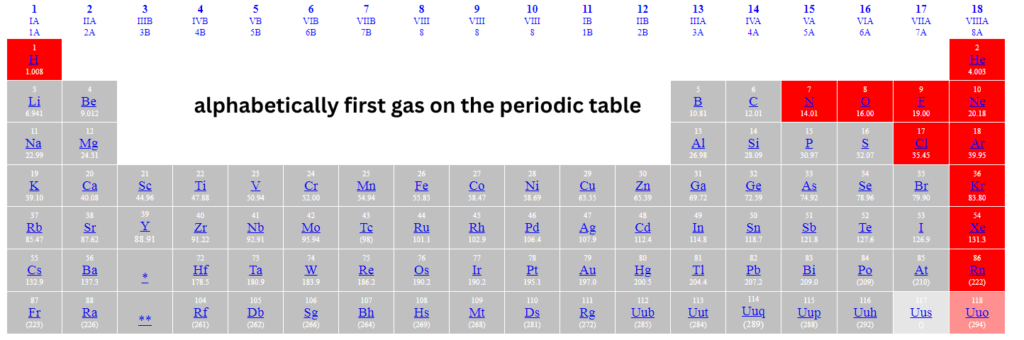
alphabetically first gas on the periodic table NYT Crossword Clue:
The NYT Crossword Clue Answers for the alphabetically first gas on the periodic table. Have you come up with a solution that leaves the clue unsolved? Fear not—we closely monitor each hint and update it with the right answers on a regular basis.Elements in Gases (stp)
ALPHABETICALLY FIRST GAS ON THE NYT Periodic Table:
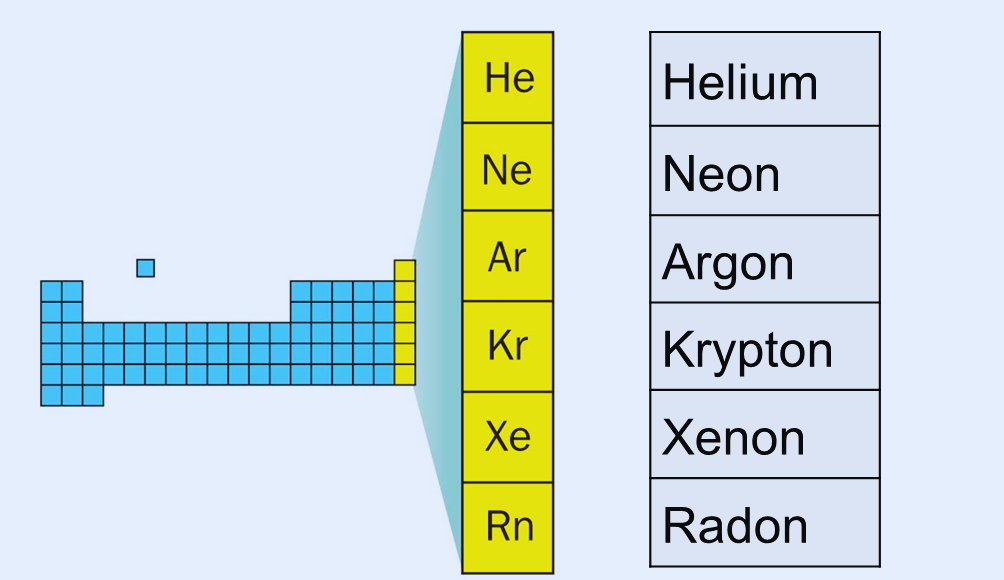
Argon alphabetically first gas on the periodic table. Here’s a closer look at this intriguing component:
Overview:
Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth’s atmosphere and a noble gas. Since it has no color, no smell, and is inert, it is generally exceedingly stable and non-reactive. It has an atomic number of 18 and is denoted by the symbol Ar.
Argon:
exists as a colorless solid, liquid, and gas. Under normal circumstances, it is a gas. When stimulated in an electric field, it gives off a vivid lilac-purple glow.
Number of Atoms: 18
Sign: Ar
Mass of an atom: 39.948(1)
Configuration of electrons: [Ne] 3s2 3p6
Group: noble gas, p-block, group 18.
Discovery:
In 1894, Sir William Ramsay and Lord Rayleigh made the discovery of argon. Studying the gases in the atmosphere allowed them to recognize it as a novel element, which eventually helped with its isolation and classification.
Isotopes:
There are several isotopes of argon, but the most common is Argon-40, which makes up around 99.6% of natural argon. Much lesser levels of other isotopes, such argon-36 and argon-38, are found.
Safety:
There are no major health dangers associated with argon because it is non-toxic. However, while dealing with it in confined places, adequate ventilation is required because it is an asphyxiant in high quantities.
Because of its inert nature, argon is extremely useful in a variety of contexts, including scientific and industrial.
Physical characteristics:
Look: Argon is a tasteless, colorless, and odorless gas.
Density: At standard temperature and pressure, it has a density of around 1.784 g/L, which is greater than that of air.
Boiling Point: -302.53°F, or -185.85°C
Melting Point: -308.83°F, or -189.34°C
Gas in the room temperature phase.
Chemical properties:
Reactivity:
Argon does not easily combine with other elements to form compounds since it is chemically inert. This is because it is stable because of its entire outer electron shell.
Uses:
Argon has many uses, such as illuminating, protecting specific chemical reactions from outside influences, and as an inert gas in welding and other industrial processes. In addition, argon is utilized in scientific studies and the manufacturing of specific kinds of electronics and glass.
Occurrence:
At roughly 0.93% by volume, argon is the third most prevalent gas in the Earth’s atmosphere. It is taken out of the atmosphere by fractionally distilling liquid air.
Because it is inert, argon is useful in a variety of contexts, including science and industry. Its continued significance in several technologies and processes is guaranteed by its function as a stable, non-reactive gas.
for more information visit our Homepage